Overview
Hot rolling is rolling above the recrystallization temperature, contrary to cold rolling which is rolling below the recrystallization temperature. To put it simply, hot rolling is a process in which the steel billet is subjected to several rounds of rolling after heating, and then trimmed and corrected into steel sheet. It can significantly reduce energy consumption and reduce costs. That is, since the metal features high plasticity and low deformation resistance during hot rolling, it can greatly reduce the energy consumption of metal deformation. Hot rolling can improve the processing performance of metals and alloys, that is, the coarse grains in the as-cast state are broken, the cracks are healed, the casting defects are reduced or eliminated, and the as-cast microstructure is transformed into a deformed structure to improve the alloy processing properties.
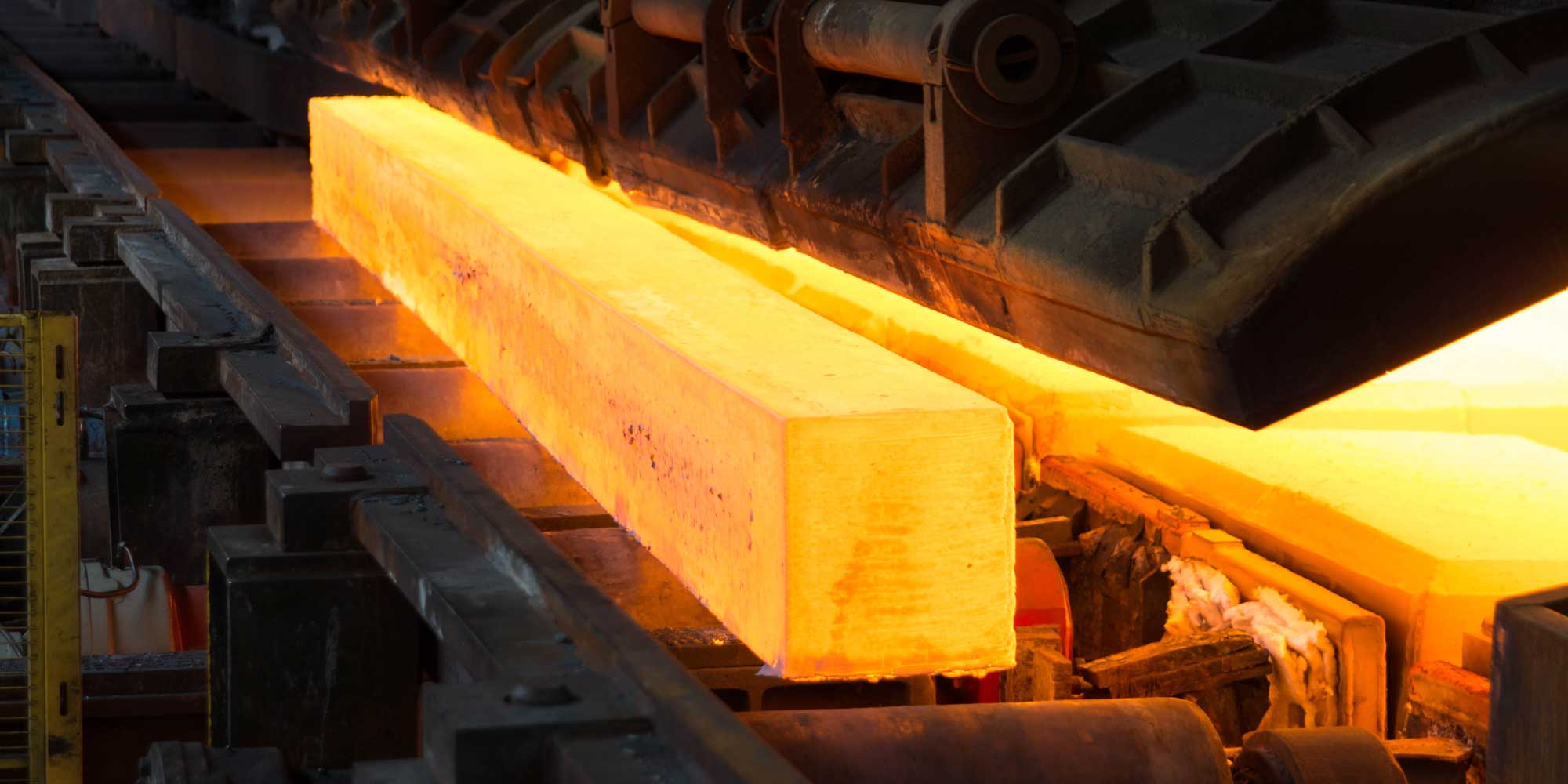

Hot rolling Concept and Features
Concept
Hot rolling refers to rolling performed above the metal recrystallization temperature.
Recrystallization is the generation of unstrained new grains (recrystallized core) in the fiber structure of deformed metal or alloy when the annealing temperature is high enough for a long time; the new grains continue to grow until the original deformed structure completely disappears and the metal or alloy properties also change significantly. This process is called recrystallization. The temperature at which new grains begin to form is called the initial recrystallization temperature. The temperature at which the microstructure is completely occupied by new grains is called the final recrystallization temperature. The generally called recrystallization temperature is the arithmetic mean of the initial recrystallization temperature and the final recrystallization temperature. The general recrystallization temperature is mainly affected by factors such as alloy composition, degree of deformation, original grain size, and annealing temperature.
Features
- 1. Low energy consumption, good plastic processing, low deformation resistance, inconspicuous work hardening, easy rolling, and reduced energy consumption for metal deformation.
- 2. Hot rolling usually adopts large ingots and high reduction rolling, featuring fast production pace and large output, which paves way for large-scale production.
- 3. The as-cast structure is transformed into a processed structure by hot rolling, and the plasticity of the material is greatly enhanced by the structure transformation.
- 4. The characteristics of the rolling method determine the anisotropy of the rolled sheets. Firstly, the longitudinal, transverse and high directions of the material have obvious performance differences. Secondly, there are deformation textures and recrystallization textures, making a clear directionality in the punching performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hot Rolling
Advantages
- (1) Hot rolling can significantly reduce energy consumption and reduce costs. The metal is high in plasticity during hot rolling, and the deformation resistance is low, which greatly reduces the energy consumption of metal deformation.
- (2) Hot rolling can improve the processing performance of metals and alloys, that is, the coarse grains in the as-cast state are broken, the cracks are healed, the casting defects are reduced or eliminated, the as-cast microstructure is transformed into a deformed structure, and the alloy processing property is thus improved.
- (3) Hot rolling usually adopts large ingots and large reduction rolling, which not only improves production efficiency, but also creates conditions for increasing rolling speed and achieving continuous and automatic rolling process.
Disadvantage
- (1) After hot rolling, non-metallic inclusions (mainly sulfides and oxides, and silicates) inside the steel are pressed into sheets, and delamination (sandwich) occurs. The delamination greatly deteriorates the steel tensile properties in the thickness direction, and it also poses risk of interlayer tearing when the welding seam is shrunk. The local strain induced by seam shrinkage often reaches several times higher than the yield point strain, much higher than the strain caused by the load.
- (2) Residual stress caused by uneven cooling. The residual stress is the internal self-balanced stress without external force. The hot-rolled steels of various sections have such residual stress. Generally, the larger the section size of the profile steel, the larger the residual stress. Although the residual stress is self-balanced, it has certain influence on the performance of steel members under external force, for instance, adverse effects on deformation, stability, fatigue, etc.
- (3) Hot rolling does not control very accurately the mechanical properties required for the product. The microstructure and properties of hot rolled products can hardly be uniform. The strength index is lower than that of the cold work hardened product but higher than the fully annealed product. The plasticity index is higher than that of the cold work hardened product but lower than the fully annealed product.
- (4) It is difficult to control the thickness of hot rolled product and the control precision is relatively poor; the rough Ra value of the hot rolled finish is generally 0.5 to 1.5 μm higher than that of cold rolled finish. Therefore, hot rolled products are generally used as blanks for cold rolling.
Applications of Hot rolled Products
- 1) General structural steels, engineering hot-rolled steel plates and strips;
- 2) welded pipes, cold rolled materials, bicycle parts, as well as important welding, riveting and bolting components.
- 3) Cold rolling and deep drawing products.
- 4) Stamping and structural parts for automobiles, tractors, engineering cranes, small light industrial machinery.
- 5) Containers and bare metal structural parts.
- 6) Pipeline for transporting oil and natural gas.
- 7) Car frames and beams.
- 8) Dedicated steel belt for automobile wheels.
- 9) Industry use skid plates, stairs, ladder pedals, etc.
Related
- Introduction of Cold Rolling Process
- What is Metal Rolling (Steel Rolling)? What is the Purpose of It?
Contact
CIVMATS Co., Ltd. produces high-value stainless steel and nickel alloy raw materials. If you want to know more about stainless steel & nickel alloy, please keep following us. Any requirements or questions about nickel alloy, call CIVMATS!
- Company: CIVMATS CO., LIMITED
- Phone: 86-519-81809659
- Fax: 86-519-81809959
- Email: sales@civmats.com
- Address: 10th Floor, Xin Cheng Nan Du, Wujin District, Jiangsu, China
- Website: www.civmats.com